
Colorectal cancer is one of the three most frequent forms in the globe.
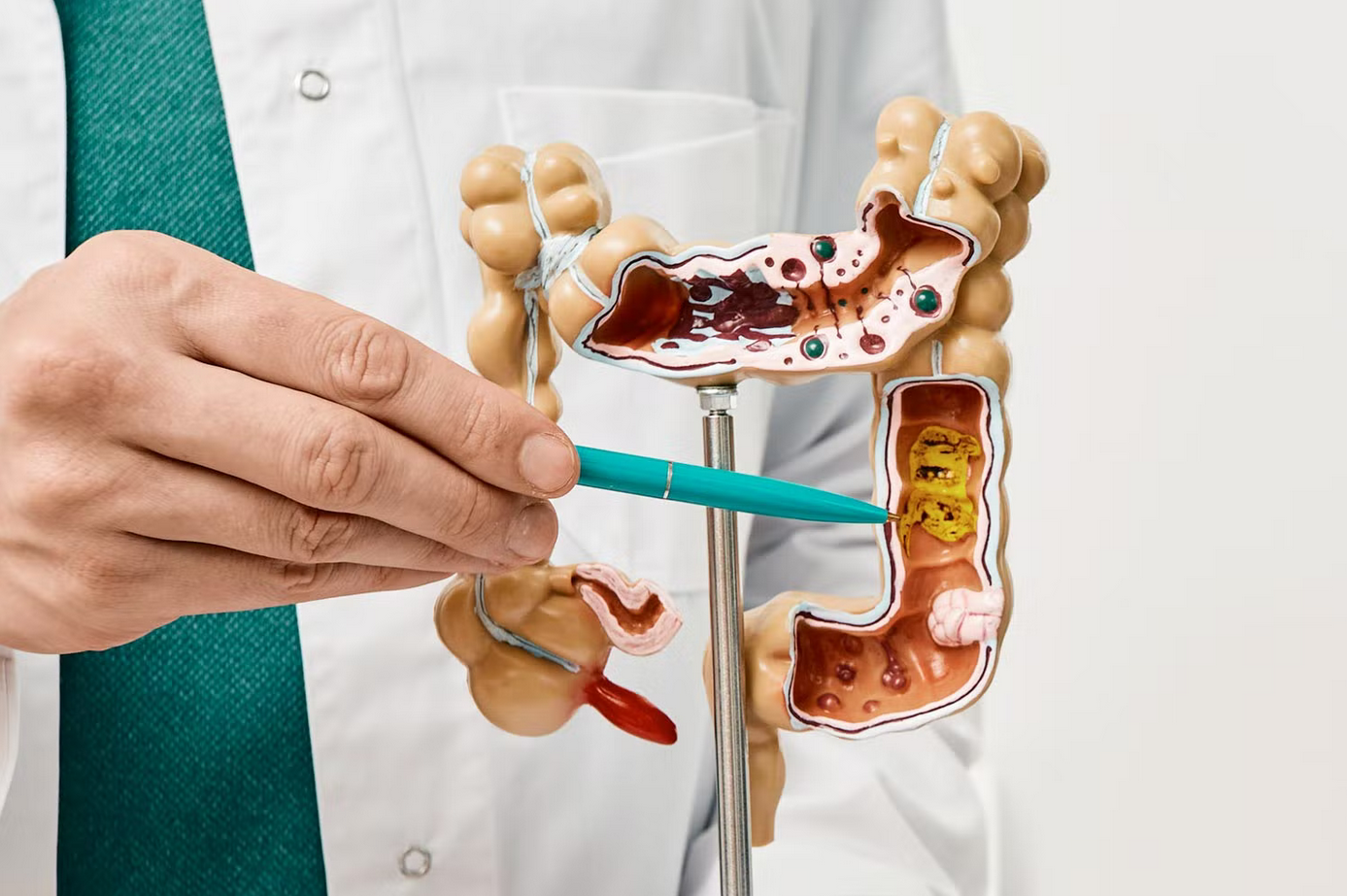
Colon cancer begins in the colon or rectum cells and spreads from there. The majority of the time, this is due to polyps in the intestines. Symptoms can not appear quickly and can range from stomach pain to blood in the stool. Colon cancer can be adenocarcinoma, colloid, or undifferentiated, depending on the cell type.
Moreover, Colorectal cancer is one of the three most frequent forms in the globe. It affects males more than women, and the majority of persons develop it beyond the age of 70. Therefore diagnosis and treatment abroad gain more popularity.


The majority of persons who are diagnosed with colon cancer have adenocarcinoma. There are many uncommon tumor kinds. These additional kinds of colon cancer may require different treatment than adenocarcinoma. The portion of this guide on colon cancer diagnosis and treatment focuses mostly on adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinoma is the most common kind of colon cancer. This is a kind of cancer that affects the cells lining the interior of the colon.
Further, Hereditary Colon Cancer is also a possibility. Colorectal cancer affects 5 to 10% of the population as a result of inherited mutations in genes that are handed down from parents to children. MSK’s colon cancer specialists may provide you with genetic testing to see whether you have inherited mutations in your genes that raise your risk of cancer.
The decision to get this testing is based on an evaluation of your personal risk. Learn more about colon cancer genetic testing and the inherited disorders that frequently cause the disease. Сolorectal lymphoma is another kind of colon cancer. Lymphoma of the colon and rectum is uncommon and can emerge as a primary colorectal lymphoma or as a complication of another disease. The majority of individuals with primary colorectal lymphoma have stomach discomfort, and blockage is rare. Although radiographic tests may reveal lesions, the findings are often vague.
Historically, aggressive B-cell lymphomas were the most often reported gastrointestinal lymphomas in the literature. Recent data, however, indicate an increase in the frequencies of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) with enhanced monitoring. 1 The majority of patients with colorectal lymphoma have surgery, although multi-agent chemotherapy remains the standard of care. B-cell lymphomas are the most aggressive, with a two-year median survival.
Colorectal cancer may not present with symptoms straight away. Many of the symptoms of colorectal cancer can, in fact, be caused by other conditions such as infection, hemorrhoids, irritable bowel syndrome, or inflammatory bowel disease. If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should seek medical attention. Many persons who exhibit these symptoms do not have cancer. However, if you experience any of these, you should consult your doctor so that the underlying reason may be identified and addressed.
The symptoms of colon cancer;
According to these facts, Colorectal malignancies frequently bleed into the stomach. Blood can sometimes be observed in the feces or cause it to appear darker, although most of the time the stool appears normal. However, blood loss can accumulate over time and result in low red blood cell levels (anemia). A low red blood cell count on a blood test can be the earliest symptom of colorectal cancer.
Some patients may show indicators of cancer spread to the liver, such as a big liver on inspection, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes), or difficulty breathing due to cancer metastasis to the lungs.
Many of these symptoms can be caused by conditions other than colorectal cancer, such as infection, hemorrhoids, or irritable bowel syndrome. Still, if you have any of these problems, it’s important to see your doctor right away so the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
Colon cancer treatment is highly dependent on how advanced it is. The tumor’s placement in the colon is also important.
Operation: When cancer is still in its early stages, a cancerous section of the intestine may typically be surgically removed. It may be traditional for colon cancer therapy or surgery without incisions. Colorectal disorders are best treated with DaVinci robotic colon surgery. This technique combines the greatest features of both open surgery and minimally invasive surgical methods.
If your colon cancer is very small, your doctor may recommend a minimally invasive approach to surgery, such as:
If your cancer is advanced or your general health is bad, your surgeon may advise you to have surgery to remove a blockage in your colon or other issues in order to alleviate your symptoms and prescribe good colon products. This surgery is not performed to treat cancer, but rather to ease symptoms such as blockage, bleeding, or discomfort.
Written by Natalia Volvak